3. Wheat Intolerance
Wheat intolerance or wheat allergy is an allergic reaction to foods
containing wheat. Wheat is one of the top eight food allergens in the USA. The
law passed in 2004 requires all food packaging to clearly list whether
they contained any of eight major food
allergens (milk, egg, peanuts, tree nuts, fish, crustacean shellfish, soy and
wheat).
If
you have a wheat allergy, allergic reactions result from eating wheat or by
inhaling wheat flour. Wheat can be found in many
foods, including some products you might not suspect, such as beer, soy sauce
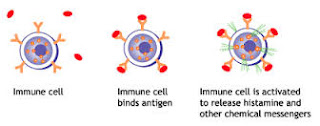
and ketchup. When a person has an allergy to a specific product, they produce a
specific allergy antibody to that product (allergen) known as IgE. This allergy
antibody coats the surface of the histamine producing cells (Mast Cells) of the
body. When the person is exposed to the allergen such as wheat the immune
response triggers the histamine producing cells to release massive amounts of
histamine and it is this chemical which causes the allergic response. That is
why people take anti-histamines to control their allergies.
A
child or adult with wheat allergy is likely to develop symptoms within minutes
to hours after eating something containing wheat. Wheat allergy symptoms
include:
- Swelling, itching or irritation of
the mouth or throat
- Hives, itchy rash or swelling of
the skin
- Nasal congestion
- Headache
- Itchy, watery eyes
- Difficulty breathing
- Cramps, nausea or vomiting
- Diarrhoea
- Anaphylaxis
- Wheat-dependent, exercise-induced
anaphylaxis
Wheat allergy sometimes is confused with celiac disease, but these
conditions differ in both cause and symptoms. A person with a wheat allergy
produces an allergy-causing antibody (different from the antibodies produced in
celiac) which reacts with certain proteins found in wheat resulting in sudden
onset allergic reaction as described above. You can develop an allergy to any of the four classes of wheat proteins —
albumin, globulin, gliadin and gluten. Avoiding wheat is the only way to prevent a wheat allergy reaction but medications may be necessary to
manage allergic reactions if wheat is accidentally ingested or inhaled.
People with celiac disease have an auto immune response to a
particular protein called gluten which is found in wheat and other grains. It
is much easier to cater for wheat free diet rather than a strict gluten free
one. But if you have a wheat allergy it is critical that you do not consume or
inhale wheat products because you could have a very serious allergic reaction.
Note: A person with a wheat allergy may
also be allergic to barley, oats and rye.
Find out more about how to achieve a gluten free diet - you can apply this advice to a diet required to manage your wheat allergy as well.



No comments:
Post a Comment